 Image credit: Original Paper
Image credit: Original PaperAbstract
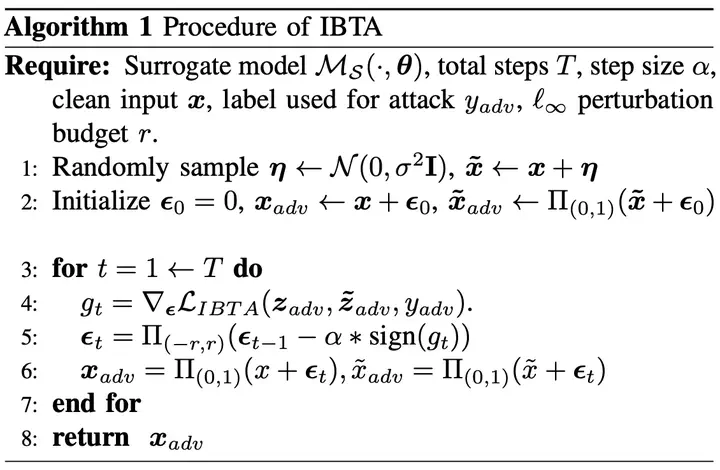
From the perspective of information bottleneck (IB) theory, we propose a novel framework for performing black-box transferable adversarial attacks named IBTA, which leverages advancements in invariant features. Intuitively, diminishing the reliance of adversarial perturbations on the original data, under equivalent attack performance constraints, encourages a greater reliance on invariant features that contributes most to classification, thereby enhancing the transferability of adversarial attacks. Building on this motivation, we redefine the optimization of transferable attacks using a novel theoretical framework that centers around IB. Specifically, to overcome the challenge of unoptimizable mutual information, we propose a simple and efficient mutual information lower bound (MILB) for approximating computation. Moreover, to quantitatively evaluate mutual information, we utilize the Mutual Information Neural Estimator (MINE) to perform a thorough analysis. Our experiments on the ImageNet dataset well demonstrate the efficiency and scalability of IBTA and derived MILB.